As cyber criminals take advantage of popular link condensing services like bit.ly and is.gd to disguise their malicious content, Twitter has responded with a link shortener of its own, which will scan the real destination of shorthand links for malicious content.
Twitter says that the new service will work a little bit differently than most of the independent link condensing services available. Instead of using a webpage to manually shorten the links, Twitter will automatically apply the service to any links – shortened or otherwise – contained in direct messages or emails.
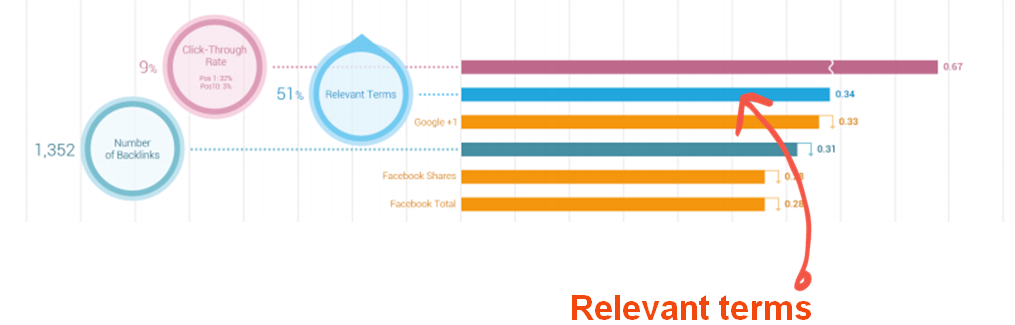
An early concern for search engine optimization (SEO) professionals was a technical one: Would the affected links – through the aforementioned automatic processing – lose SEO relevance? Danny Sullivan of Search Engine Land reports that, for the moment, the links appear to be intact: "No link juice is lost," he says.
However, Sullivan notes that Twitter could consider applying the system to all links on its service, which could complicate search engine optimization (SEO) if it changes even a little.