Google has announced its latest update that will break the search mold of matching keywords to queries. The company’s Knowledge Graph attempts to revolutionize search by making its engine “understand the world a bit more like humans do.” The update is a step toward giving users relevant, meaningful answers to searches instead of results that seem to match queries – completely changing SEO and supporting Google’s effort to become a “knowledge engine” instead of an “information portal.”
Building the bridge between queries and meanings
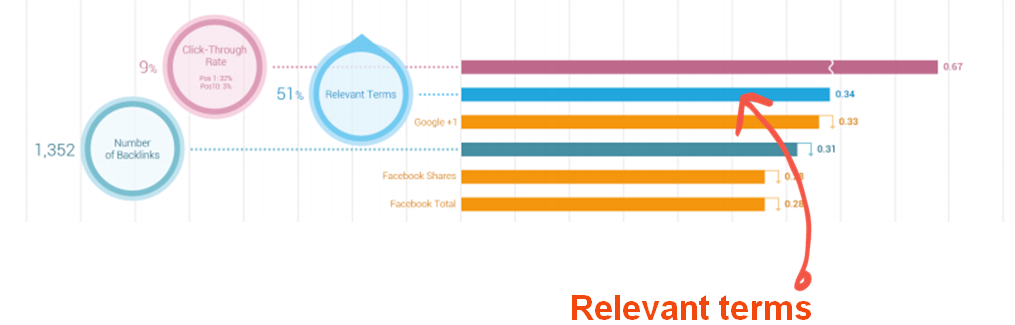
The Knowledge Graph helps Google understand the meaning of queries and the relationships between different objects in the real world. Google explains that the goal of the Graph is to collect information about different real-world entities (like a book, a product or a person) so that the search engine will be able to provide the best answers by combining info it deems relevant and info other searchers’ have marked as useful on that topic. Among other things, the Graph seems to incorporate more search history and aggregate social data into results, with Google indicating it draws on “collective human wisdom.” The update seems to shed light on Matt Cutts’ recent Webmaster Central video that carefully explained Google’s use of human raters in search ranking.
In a video announcement of the Graph, Google’s Jack Menzel said, “If we can understand that [queries] are talking about real-world things, then we can do a better job of getting you just the content that you want off the web.” This mirrors an earlier statement from Menzel about SEO and the rise of the interactive web. Brafton quoted him at SMX West as saying that Google “wants the web to be about conversations” to provide contextual answers and meaningful content.
The Knowledge Graph and the changing the nature of SEO
The Knowlege Graph tries to treat web entities as objects in the real world. The company explains this means Google search attempts to understand the relationships between “things, not strings” which SEO marketers might interpret as an emphasis on contextual relevance over links. “As we grow the knowledge graph, we’re excited at the opportunity we have to understand users queries, to understand the information on the web and intelligently connect the two,” said Sashi Thakur, technology lead.
This brings to mind the contextual markup tool, schema.org, which Google has supported in the past. Though, as Search Engine Land reported, Google’s Matt Cutts has advocated rel=author above schema.org to help sites build contextual authority through their content writers. The update suggests site owners and marketers must strongly consider adding rel=author to build brand authority in their niche.
Social data will wield more influence in what ranks for searches with this update. As product manager Emily Moxley explained, Google will “jumpstart [searchers’] research by combining the information that others found useful with information in the Knowledge Graph.” The company says people’s activity will inform what it puts in the database.
Three initial Knowledge Graph elements that impact search
Google’s Amit Singhal broke down the first three features that will roll out as part of the Knowledge Graph.
- Smarter interpretation of search queries: The Knowledge graph will help Google understand the meaning of words users type in based on their real-life meanings. Google presents a side bar with different interpretations of search query meanings, and users can narrow their results by clicking the interpretation that is relevant to them.
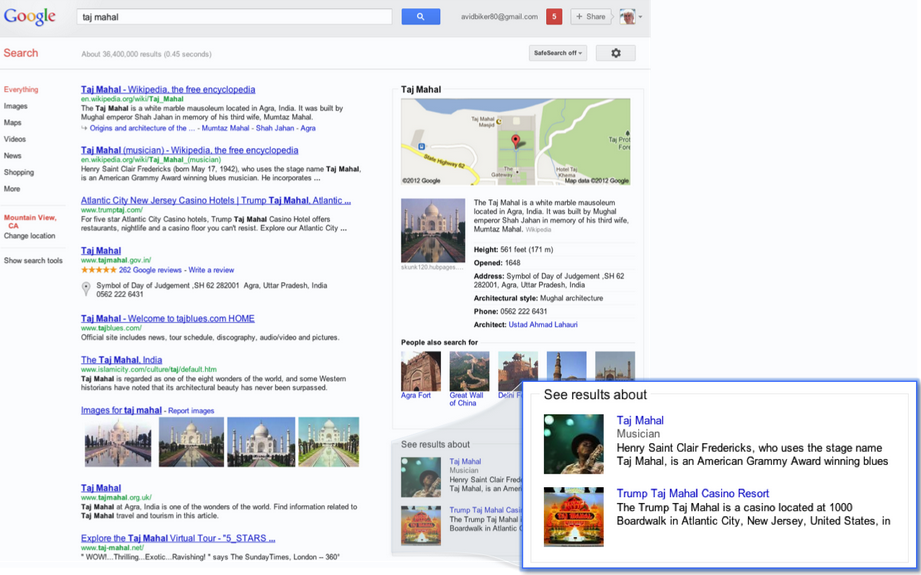
- More contextual information around results: Continuing its rising tradition of putting answers directly on SERPs, the Knowledge Graph gives users summaries of the core details around their searches. The information included in summaries is based on Google’s studies of aggregate searches conducted around specific queries.
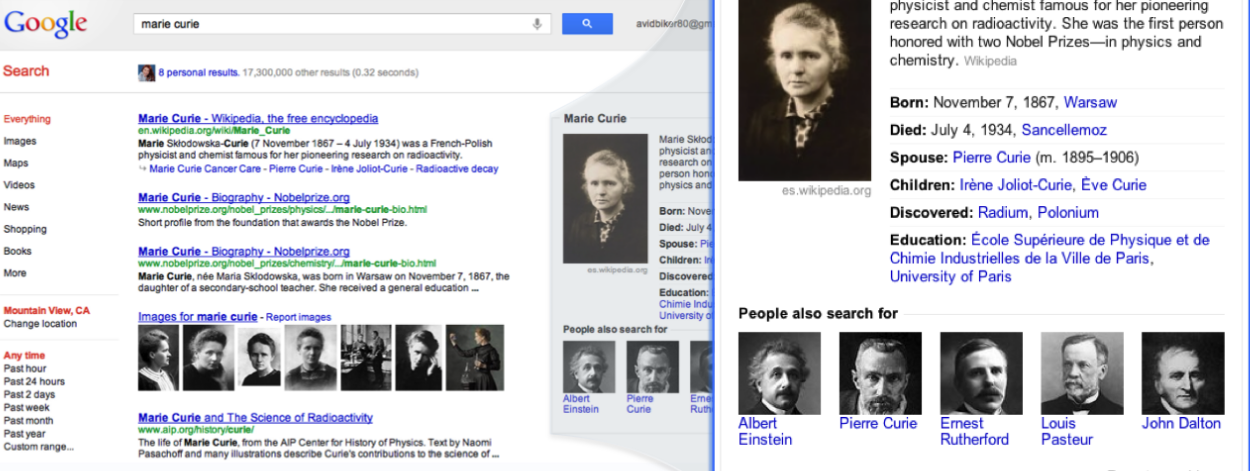
- Discovery through search: Google provides information for search queries to give users additional facts and make them aware of unexpected connections. In some cases, this feature may answer questions that would have merited follow-up searches, and in other instances Google says it could start a whole new line of searches. Singhal explains:
We’ve always believed that the perfect search engine should understand exactly what you mean and give you back exactly what you want. And we can now sometimes help answer your next question before you’ve asked it, because the facts we show are informed by what other people have searched for.
Google’s move toward a search landscape that gives users “exactly what [they] want” is an indication that sites looking to gain visibility on the web will have to work on the same principle of satisfying users.
Search enhancements from the Knowledge Graph are being rolled out gradually, and Google says smartphone- and tablet-friendly versions will soon be available. Marketers can learn more about the Knowledge Graph in the official video announcement.